 |  |  |
|
|
Gallery
Tips
| About Bulgaria Bulgarian Flag  Bulgarian Coat of arms Bulgaria is situated in the South-Eastern part of the Balkan Peninsula. It borders Greece and Turkey to the South, Macedonia and Serbia - to the West. The Danube River to the North is our natural border with Romania; the Black Sea is situated to the East. The country has an area of 110,910 km² spreading from its mountainous regions in the West through amazing plains and valleys to the Black Sea on its Eastern border. Bulgaria’s landscape and scenery is utterly breathtaking. Bulgaria has a population of 7.64 million (2008 est.) the majority of whom reside in the major urban areas such as Sofia, Plovdiv, Varna, etc. The main language is Bulgarian with English and Russian also being widely spoken as second language. 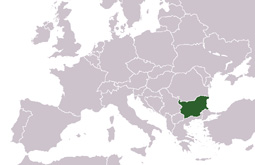 Location of Bulgaria in Europe 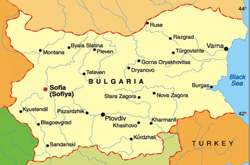 Location of Bulgarian Capital Sofia and other cities History. The history of Bulgaria goes back more than 3,000 years. A succession of various civilizations, Thracian, Roman, and Byzantine, the Bulgarian state has now existed for more than 13 centuries on the Balkan Peninsula which has long been a meeting place and a melting-pot of tribes and nations. The Bulgarian state was founded in 681 AD, when Slavs and Proto-Bulgarians were brought together under the sceptre of the Khan.  Nature  Nature The conversion of the Bulgarians to Christianity in 865 AD joined Bulgaria to the Christian civilization. The invention of the Cyrillic script in the latter half of the ninth century, in an age when Latin and Greek predominated in public and holy writings, gave a powerful impetus to the country's cultural development. In 1185, after a number of battles with Byzantines, the noble brothers Assen and Peter led a revolt that forced Byzantine recognition of an autonomous Bulgarian state. The Second Bulgarian Empire was centred in today's town of Veliko Turnovo. In 1202 Tsar Kaloian (1197-1207) concluded a final peace agreement with Byzantium that gave Bulgaria full independence, which contributed to the flourish of the Bulgarian culture. After the death of Ivan Asen II, political instability threatened the Bulgarians.  Nature  Nature Unfortunately, in 1396 Bulgaria fell under Turkish slavery whose occupation of the Bulgarian lands continued nearly 500 years. The preparation for the national liberation began in the early 18600’s under the leadership of Georgi Sava Rakovski (1821 - 1867) and Vassil Levski (1837 - 1873). The War of Liberation (the Russian-Turkish War) regained Bulgaria's freedom in 1878. In 1879 the Constituent Assembly adopted the first constitution of Bulgaria - one of the most democratic constitutions of the day. The first decades of the 20th century were years of economic effort and prosperity. Bulgarian goods and the Bulgarian currency, the 'Golden Lev', acquired a high value on the European markets. Trade relations with Austria, Germany, France and Great Britain strengthened.  Sofia Sheraton  Palace Government. Bulgaria is a parliamentary republic and conforms to the Constitution of the Republic passed by the Grand National Assembly in July 1991. The Constitution of the Republic of Bulgaria is the supreme law of the country and no other law may contravene it. All international treaties, which are ratified pursuant to the constitutional procedure, are considered part of the domestic legislation. The National Assembly is a one-chamber parliament. It consists of 240 Members of Parliament who are directly elected every four years. The National Assembly is a permanent acting body, directed by a board of Chairmen including a Chairman of the National Assembly.  Alexander Nevsky Cathedral  Architecture The head of the state is the President, who embodies the unity of the nation and represents the Republic of Bulgaria in its international relations. The Council of Ministers is the executive state body and directs the domestic and foreign policy of the country. The government manages the implementation of the state budget, organizes the management of state property and approves or rescinds certain categories of international treaties pointed out in the Constitution.  Architecture  Sofia Vitosha Under the democratic process, there has been a smooth transfer of power, strengthening of state institutions and a consensus amongst all political parties towards promoting the market economy and respecting human rights. | Testimonials
|


